Effective Strategies for Managing Atopic Dermatitis in Older Adults
Atopic Dermatitis (AD), commonly known as eczema, is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that affects millions globally, including a growing number of older adults. Managing AD in seniors requires a tailored approach due to age-related skin changes and other health considerations.
Atopic Dermatitis (AD), commonly known as eczema, is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that affects millions globally, including a growing number of older adults. Managing AD in seniors requires a tailored approach due to age-related skin changes and other health considerations.
This article explores the causes, symptoms, and effective management strategies to help seniors live more comfortably with this condition.
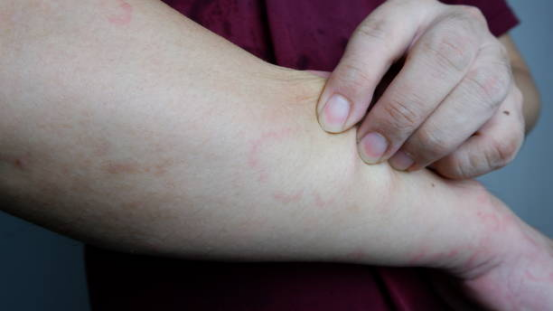
Understanding Atopic Dermatitis
Atopic Dermatitis is a persistent skin disorder characterized by dry, itchy, and inflamed skin. While it can affect individuals of all ages, seniors often face unique challenges due to natural aging processes, such as thinning skin, reduced moisture retention, and a weakened immune system. These factors can make AD more severe and harder to manage in older adults.
The Unique Challenges for Seniors
Aging skin is more vulnerable to irritation and damage, making seniors particularly susceptible to the discomfort of AD. The constant itching and inflammation can lead to sleep disturbances, emotional distress, and a reduced quality of life. Additionally, the psychological burden of dealing with a chronic condition like AD can create a cycle of stress and worsening symptoms.
Identifying Common Triggers
To effectively manage AD, it’s essential to recognize and avoid common triggers. These include:
- Environmental Factors: Cold, dry weather can exacerbate symptoms, while excessive heat and sweating can also irritate the skin.
- Allergens: Pollen, dust mites, and pet dander are frequent culprits.
- Irritants: Harsh soaps, detergents, and synthetic fabrics can aggravate sensitive skin.
- Stress: Emotional stress is a well-known trigger that can worsen AD symptoms.
Comprehensive Management Strategies
Managing AD in seniors requires a multifaceted approach that combines skincare, medical treatments, and lifestyle adjustments. Here are some proven strategies:
1. Daily Skincare Routine:
- Use gentle, fragrance-free cleansers and moisturizers to maintain skin hydration.
- Apply moisturizer immediately after bathing to lock in moisture.
2. Medical Treatments:
Topical Corticosteroids: These are commonly prescribed to reduce inflammation and itching.
Calcineurin Inhibitors: Non-steroidal creams that help control inflammation.
Antihistamines: Useful for managing itching, especially at night.
Phototherapy: UV light therapy can be effective for moderate to severe cases.
3. Lifestyle Adjustments:
- Wear soft, breathable fabrics like cotton to minimize skin irritation.
- Avoid known triggers and allergens.
- Maintain a balanced diet and stay hydrated to support overall skin health.
Preventing Flare-Ups
Prevention is key to managing AD effectively. Seniors can take proactive steps to reduce the frequency and severity of flare-ups:
- Moisturize Regularly: Keep skin hydrated with emollients and ointments.
- Track Triggers: Maintain a symptom diary to identify and avoid potential triggers.
- Stress Management: Incorporate relaxation techniques such as meditation or gentle exercise to reduce stress.
When to Seek Professional Help
While mild AD can often be managed at home, it’s important to consult a healthcare provider if:
- Symptoms persist or worsen despite treatment.
- Over-the-counter remedies are ineffective.
- Signs of infection, such as redness, swelling, or pus, appear.
Key Takeaways for Seniors with Atopic Dermatitis
- Prioritize skin hydration with regular moisturizing.
- Avoid known irritants and allergens.
- Seek medical advice for persistent or severe symptoms.
- Adopt a holistic approach that includes stress management and a healthy lifestyle.
Living Well with Atopic Dermatitis
While AD is a chronic condition with no cure, it can be effectively managed with the right strategies. For seniors, understanding the unique challenges of aging skin and implementing a personalized care plan can significantly improve comfort and quality of life. With proper management, seniors can enjoy their later years with greater ease and confidence.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is Atopic Dermatitis curable?
A: There is no cure for AD, but it can be managed effectively with proper treatment and lifestyle adjustments.
Are natural remedies helpful for AD?
A: Some natural remedies, such as oatmeal baths or coconut oil, may provide relief, but always consult a healthcare provider before trying new treatments.
Can diet influence Atopic Dermatitis?
A: While diet is not a direct cause, certain foods may trigger symptoms in some individuals. Keeping a food diary can help identify potential triggers.
Is Atopic Dermatitis contagious?
A: No, AD is not contagious and cannot be spread to others.
How does stress affect AD?
A: Stress can worsen AD symptoms, making stress management an important part of treatment.
By adopting these strategies, seniors can better manage Atopic Dermatitis and enjoy a more comfortable and fulfilling life.